Describe the Structure and Function of Arteries Capillaries and Veins
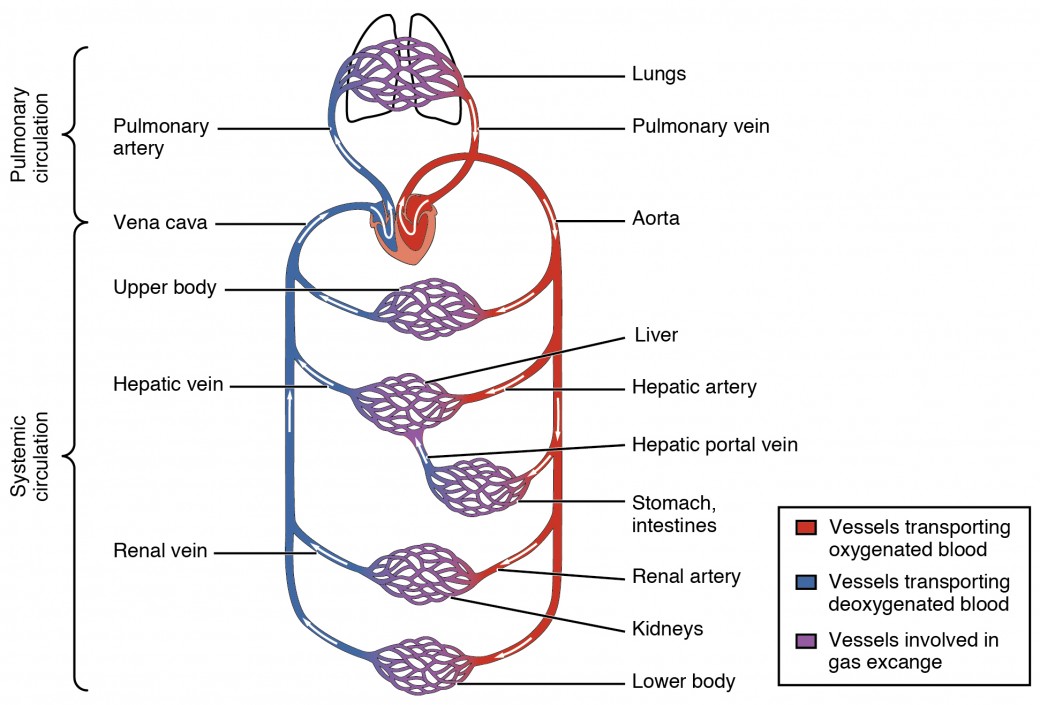
Pulmonary arteries transport blood that has a low oxygen content from the right ventricle to the lungs. Arteries are defined as the blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the tissues.
Discuss the 2 venous return mechanisms.

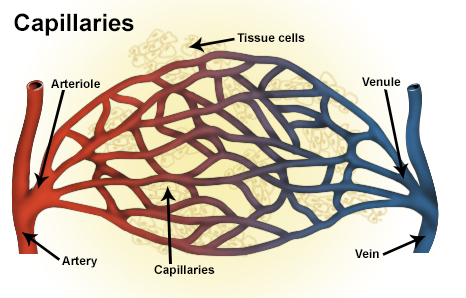
. These vessels are often referred to as the microcirculation Only two layers of cells thick the purpose of capillaries is to play the central role in the circulation delivering oxygen in the blood to the tissues and picking up carbon dioxide to be eliminated. The overall function of the circulatory system is to transport blood and lymph around the body. I intend to explore the structure and function of arteries veins and capillaries.
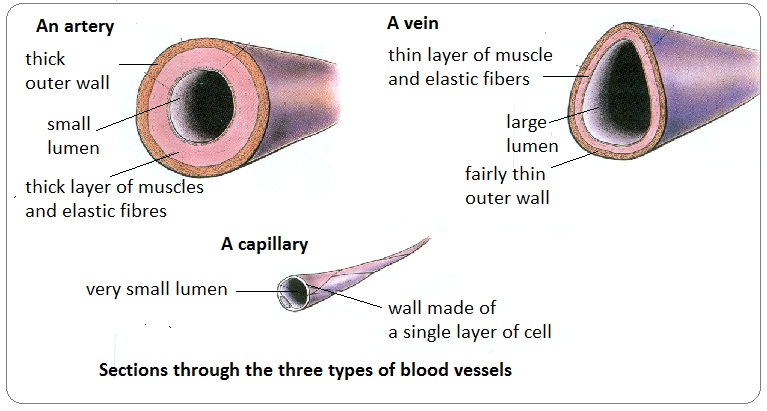
The capillaries also connect the branches of arteries and to the branches of veins. -continuously divide into medium and branch out into the body. Arteries - Function Structure of Wall Lumen and Valves Function - Carry blood away from the heart at high pressure Structure of wall - Outer wall of elastic fibres and an inner wall containing smooth muscle with some elastic fibres.
On the other hand veins are defined as the vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from organs back to the heart. Based on their structure and function blood vessels are classified as either arteries capillaries or veins. The systemic circuit and the pulmonary circuit Figure 2011.
-medium arteries further branch. Coronary arteries likewise assist the heart in pumping blood by sending out oxygenated blood to the heart enabling the muscles to function. Arteries and veins transport blood in two distinct circuits.
Blood is transported in arteries veins and. Larger arteries and veins contain small blood vessels within their walls known as the vasa vasorumliterally vessels of the vesselto provide them with this critical exchange. Arteries carry blood to other organs of the body.
It is returned to the heart in the veins. In doing so it delivers oxygen and nutrients to the body removes waste products from the body is involved in the. Veins return blood back toward the heart.
The structure and function of the heart arteries veins and capillaries is vital for the circulatory system to work. The capillaries connect the two types of blood. Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
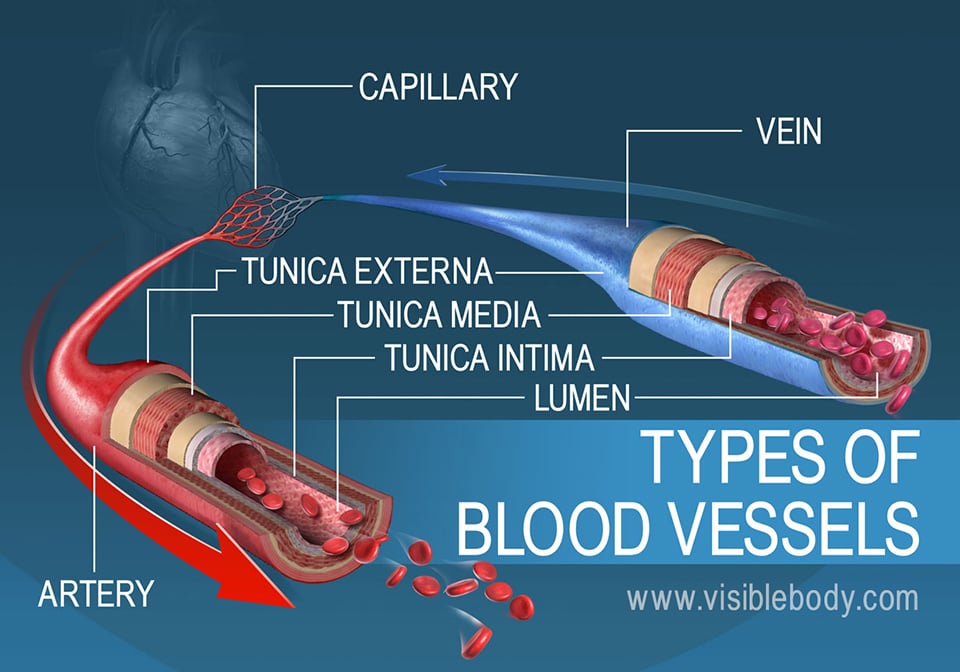
Tunica media middle layer is the region where the blood vessels consist of smooth muscle and elastin fibres and the tunica adventitia. The tunica externa the tunica media and the tunica. Five main types of blood vessels.
JOHN BAVOSIScience Photo LibraryGetty Images. Arteries are surrounded by much more muscle in the tunica externa and tunica media compared to veins. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the tissues except for pulmonary arteries which carry blood to the lungs for oxygenation generally veins carry deoxygenated blood to the heart however the pulmonary veins carry.
Arteries arterioles capillaries venules and veins. Blood is pumped from the heart in the arteries. Be sure to describe both the structure and function of each.
The basic overall structure for veins and arteries is including the tunica intima they have an additional two tunics. Vessel networks deliver blood to all tissues in a directed and regulated manner. Arteries are components of the cardiovascular system.
Capillaries connect the arterial system which includes the blood vessels that carry blood away from your heart to your venous system. Your venous system includes the blood vessels that. Well explain the basic structure of a vein.
4 rows Blood pumped by the heart flows through a series of vessels known as arteries arterioles. Capillaries transport blood between arteries and veins. This is the opposite function of veins which transport blood to the heart.
The walls of most blood vessels have three distinct layers. Structure and function of arteries capillaries and veins. Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to the body.
Blood vessels consist of arteries arterioles capillaries venules and veins. An artery is an elastic blood vessel that transports blood away from the heart. Arteries are the blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood to the bodys tissues.
Your venous system is a network of veins that carry blood back to your heart from other organs. Eventually the smallest arteries vessels called arterioles further branch into tiny capillaries where nutrients and wastes are exchanged and then combine with other vessels that exit capillaries to form venules small blood vessels that carry blood to a vein a larger blood vessel that returns blood to the heart. Describe the structure and function of the arteries veins and capillaries.
Arteries and veins are composed of three tissue layers. Systemic arteries provide blood rich in oxygen to the bodys tissues. Systemic arteries transport oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body tissues.
Arteries are the largest blood vessels with the thickest walls and capillaries are the smallest. Arteries Thick walls with small lumens. Differentiate the types of blood vessels arteries veins capillaries.
Capillaries come together to form venules small blood vessels that carry blood to a vein a larger blood vessel that returns blood to the heart. The thick outermost layer of a vessel tunica adventitia or tunica externa is made of connective tissue. Capillaries surround body cells and tissues to deliver and absorb oxygen nutrients and other substances.
Structure and function of blood vessels. Our cardiovascular system is made up of the heart blood vessels. The Structure and Function Of Arteries Veins and Capillaries In its route from the heart to the tissues the blood passes through channels of six foremost types.
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in the body connecting the smallest arteries to the smallest veins. Elastic arteries muscular arteries arterioles capillaries venules and veins. How they are similar and how they differ.
-A blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart. On the other hand capillaries are defined as the smallest vessels that link arteries and veins. Since the pressure within arteries is relatively high the vasa vasorum must function in the outer layers of the vessel see Figure 622 or the pressure exerted by the blood passing through the vessel.
Blood Vessels Circulatory Anatomy

Arteries Veins And Capillaries Arteries And Veins Arteries Human Anatomy And Physiology

Concept 1 Review Structure And Function Of Arteries Capillaries And Veins From Phschool Com Arteries Human Anatomy And Physiology Human Body Anatomy

What Are Capillaries Human Anatomy And Physiology Body Tissues Human Body Anatomy
Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Learn About Structure And Function Of Arteries Veins Capillaries And Lymphatic Vessels Differences Between Elastic Medical Videos Medical Education Medical

Medical School Cross Section Of An Artery Vein And Capillary Arteries Physical Education Lessons Arteries And Veins

Biology Notes For Igcse 2014 72 Arteries Veins And Capillaries Structure And Functions Arteries And Veins Human Circulatory System Arteries
Seer Training Classification Structure Of Blood Vessels

Medical Illustration Stock Photos Images Pictures Human Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy Medical Laboratory

Veins Capillaries Arteries By Discipline Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical Knowledge Health Science Education

Heart And Cardio Anatomy Poster Etsy Cardiovascular System Human Anatomy Nervous System Anatomy
Structure And Function Of The Heart Arteries Veins Capillaries Hsc Pdhpe







Comments
Post a Comment